Theme:
Stroke Meet 2019
ME Conferences has overcome to report the initiation of "6th Annual Conference on Stroke and Neurological Disorders" to be held on December 02-03, 2019 at Rome, Italy with the creative topic “New Emerging Drifts and Tactics on Stroke and Neurological Disorders".
ME Conferences organizes a progression of gatherings of 1000+ worldwide Events inclusive of 1000+ Conferences, 500+ future and previous Symposiums and Workshops in the USA, Europe and Asia with help from a thousand extra logical social orders and distributes 700+ Open access Journals that contains more than 50000 prominent identities, recognized researchers as publication board individuals
This creative gathering talks about the headings of Neurological Disorders, Stroke with advanced Neuroscience in this quick moving and creating science and invention. Yearly Conference on Stroke and Neurological Disorders gives the extension chances to find out about most recent modernizations, therapeutic practices and principally centers around spreading the mindfulness about how to counteract stroke and neurological issue and different difficulties in the field of neuroscience.
We are forestalling an incredible social affair of researchers, inquire about researchers, specialists, doctors, logical workforce, pharmaceutical ventures, producers and more crowd from worldwide.
WHY TO ATTEND?
STROKE MEET 2019 offers the best platform to study, inform and discuss new thoughts, current encounters, medicines, failures and issues related to neurological disorders as well as stroke. It is proceeded by knowledgeable, expert and practiced Neurologists, Neuroscientists, neuro health authorities, neurology nurses and hospitals, stroke consultants, neuro-researchers, neuro health care associates, pharmaceutical companies and a team of many other multidisciplinary authorities and medical device manufacturing company. Stroke Meet 2019 Conference goal is gathering universal experts and eminent people to share and discuss their novel ideas and research work so that it would be beneficial for patients suffering from stroke and neurological disorders. Stroke Meet 2019 objective is to gather the audience from everywhere throughout the world to present current research and to broadcast the new trends in the field of stroke and neurology.
It will be a great platform for the young potential researchers and delegates to breakout sessions, highlighting clinical projects, education, and research studies and also to gain vast knowledge from the Discussion with the Neurologists.
We similarly respect the partnership of scientists, research scholars, surgeons, physicians, science faculty and more spectators, Presidents, CEO's, Delegates and Industrial administrators from Pharmacy and Health care divisions making the summit an ideal stage to arrange, share outlooks and information through interactive keynote, plenary, posters and B2B debates.
TARGET AUDIENCE
- Neurologists
- Neurosurgeons Pharmacists
- Neurology Nurses
- Specialists in neuroscience medicine
- Academic Professionals
- Research Scholars
- Pharmaceutical Companies
- Primary care doctors
- Primary care professionals
- Nurses
- Students
- Associations and Societies
- Physicians and Faculty
- Medical Colleges
- Neurorehabilitation Physicians
- Training Institutes
- Manufacturing Medical Devices Companies
- Hospital Administrators
- Hospital General Counsel
- Business Delegates
- Neurology Faculty and Students
Track 1: Stroke and Mental Health
Though the effects of stroke are unpredictable, mood disorders such as depression, anxiety and pseudo-bulbar affect (PBA) are equally common. Researchers are actively investigating if certain kinds of strokes or strokes in certain areas of the brain produce mood disorders. So far, studies suggest that simply having a stroke increases the risk of either anxiety or depression, or having both. Research indicates that PBA is more common in survivors of the brainstem stroke, but it can occur in strokes in other areas. Depression influences somewhere in the range of one-and 66% of stroke survivors. It is characterized by feelings of sadness, lack of pleasure in activities that were before enjoyed, also changes in eating and sleeping patterns. On different hands, anxiety happens when a survivor focuses around stresses and concerns. “They go over them again and again in their minds but without necessarily reaching a conclusion. Anxiety affects about 20 per cent of survivors. PBA is characterized by a mismatch between feelings and expression i.e., laughing at a funeral, crying for a joke. PBA hasn't been examined as much as depression or anxiety, however, it's normal, affecting 28 to 52 per cent of stroke survivors, as indicated by studies. Mood disorders significantly alter the lives of survivors and their families. Because crying or a lack of emotions characterize the disorders, it’s best to identify them accurately and receive treatment based on a psychological assessment. The mental health professionals talk with the survivors to determine the condition of their mind and their behaviour.
Track 2: Neurological Disorders
As per the survey, there are in excess of 600 neurological disorders. Neurological Disorders are diseases that influence the brain and the central nervous systems. In recognizing the signs and symptoms of neurological problems, it is first important to differentiate the many types of neurological disorders. The World Health Organization reports that different kinds of neurological disorders influence a huge number of individuals around the world, including 24 million that experience from Alzheimer’s disease and 326 million who experience migraines. If you suspect that you or a loved one may be suffering from one of these issues, you may also be wondering about what causes a neurological disorder. The causes of such dysfunction can be quite diverse. Both the spinal cord and brain are insulated by abundant membranes that can be vulnerable to force and pressure. The peripheral nerves located deep under the skin can also be vulnerable to damage. Neurological disorders can affect a whole neurological pathway or a single neuron. Even a small disturbance to a neuron’s structural pathway can result in dysfunction.
Track 3: Stroke and Cardiovascular Diseases
Cerebrovascular disease is a health disorder that affects the blood vessels of the brain and cerebral circulation. The arteries providing oxygen and nutrients to the brain are usually getting injured in these disorders. The most communal type of cerebrovascular disease is an ischemic stroke or mini-stroke and sometimes a haemorrhagic stroke. Hypertension is the most significant contributing risk factor for stroke and cerebrovascular diseases as it can change the structure of blood vessels and result in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a disorder where the blood vessels narrow in the brain, resulting in reduced cerebral perfusion. Narrowed cerebral arteries may lead to ischemic stroke, but continually elevated blood pressure can also cause tearing of vessels, leading to a haemorrhagic stroke. Stroke is a dangerous factor for coronary heart disease. Coronary heart disease and stroke share many of the similar risk factors such as high LDL cholesterol levels, low HDL cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, physical inactivity, and being heavy weight or obese. Persons with coronary heart disease, angina, or who have had a heart attack due to atherosclerosis, have more than twice the risk of stroke than those who haven’t. If you have atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries you are very likely to have atherosclerosis in other portions of your body. Atherosclerosis is often referred to as "hardening of the arteries." The word comes from the Greek words athero (gruel or paste) and sclerosis (hardness). In atrial fibrillation, the upper chamber of the heart (the atria) shiver instead of beating efficiently to move blood into the ventricle.
Track 4: Brain and Neuromuscular Diseases
A healthy brain and nervous system regulate your body functions so you can have full command over your senses, muscles, and intelligence. In spite of the amazing capacities of the human brain and nerves, they are vulnerable to damage just like every other part of our bodies. Strokes, concussions, Alzheimer’s and many other brain problems disturb about 50 million Americans. Brain Injuries and illnesses strike dissimilar people based on the risk factors of their genetics, age and lifestyle. The severity of damage and the availability of action vary widely. Facts of brain and nerve health has progressed rapidly in recent years. Many new treatments and medicines are available to treat various disorders. Still, the best thing for your brain is to possess it physically and mentally active while eating nutritious food and getting abundantly of social interaction. Neuromuscular diseases are a wide-ranging collection of diseases that distress nerves and muscles. They can rise following an injury, from other diseases such as diabetes, or from inherited or autoimmune diseases. Neuromuscular diseases can cause pain, faintness, numbness, and occasionally more severe symptoms such as difficult in talking, eating, or breathing. Neuromuscular diseases include Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Lou Gehrig's Disease), Guillain Barre syndrome, Muscular dystrophy, Myasthenia gravis, Myopathy.
Track 5: Stroke Rehabilitation and Recovery
Rehabilitation is given for a long period of time to recover function so that the stroke survivor can become as self-governing as possible. This must be skilled in a way that conserves dignity and motivates the survivor to relearn basic skills that the stroke may have impaired - skills like bathing, eating, dressing and walking. Rehabilitation starts in the hospital as soon as probable following a stroke. The rehab squad includes Physiatrist, Neurologist, Rehabilitation Nurse, Physical Therapist, Occupational Therapist and Speech-Language Pathologists. Recovery following a stroke starts as the brain responds to what’s happened. The brain’s functions will be adjusted to account for the death or decrease in the affected area. If a stroke victim gets medical attention within three hours of suffering the stroke they may be a entrant to accept medication to break up clots via an IV-drip. This clot-destroying medicine can significantly reduce long-term disabilities in the patient. The rehabilitation process begins after doctors have evaluated and treated any critical conditions in the patient, and taken precautionary steps to prevent extra complications. This means rehabilitation could commence during the patient’s first hospital visit, which will increase the probability of recovering the damaged body and brain function. The first three months of recovery are when a patient will see the most progress, and gains may happen rapidly over time. Some stroke survivors will continue to progress after this period; however, if the brain stem was affected during the stroke recovery could take up to a year or even longer.
Track 6: Epidemiology
Epidemiology is a scientific discipline with sound approaches of scientific inquiry at its foundation. Epidemiology is data-driven and relies on a systematic and unbiased method to the collection, analysis, and clarification of data. Basic epidemiologic procedures tend to rely on the careful remark and use of valid comparison groups to assess whether what was experimental, such as the number of cases of the disease in a specific area during a specific time period or the occurrence of exposure among persons with the disease, differs from what might be expected. Though, epidemiology also draws on methods from other scientific arenas, including biostatistics and informatics, with biologic, economic, social, and behavioral sciences. In fact, epidemiology is often defined as the basic science of public health, and for good reason. First, epidemiology is a quantitative discipline that count on on a working knowledge of probability, statistics, and sound research approaches. Secondly, epidemiology is a way of fundamental intellectual based on emerging and testing premises grounded in such scientific fields as biology, behavioral sciences, physics, and ergonomics to enlighten health-related behaviors, states, and events. Yet, epidemiology is not just a study action but an integral factor of public health, providing the foundation for directing applied and suitable public health action based on this science and causal reasoning.
Track 7: Neurophysiology and Neurodegeneration
Neurophysiology is a division of physiology and neuroscience that is concerned with the learning of the functioning of the nervous system. The primary tools of neurophysiological research hold electrophysiological copies, for instance, voltage clamp, patch clamp, extracellular single-unit recording and recording of local field potentials, as well as some of the means of apoptogens, calcium imaging, and molecular biology. Neurophysiology is correlated to electrophysiology, neuroanatomy, psychology and mathematical neuroscience. Neurodegeneration is the process of progressive injury of structure or role of neurons, with the death of neurons. Several neurodegenerative diseases – including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and Huntington's – occur as a effect of neurodegenerative processes. Such diseases are incurable, subsequent in progressive degeneration and/or death of neuron cells. As study progresses, many similarities seem that relate these diseases to one another on a sub-cellular level. Discovering these resemblances offers hope for therapeutic advances that could ameliorate numerous diseases instantaneously. There are many equivalents between different neurodegenerative disorders including atypical protein assemblies as well as induced cell death. Neurodegeneration can be found in several diverse levels of neuronal circuitry oscillating from molecular to systemic.
Track 8: Brain Tumor and Neuro-oncology
Benign and malignant. Benign tumours are usually formed by slow-growing cells that hardly spread. However they can press on and harm nearby normal tissue. Benign tumours are less dangerous than malignant tumours. Though, they can be dangerous if they endanger vital brain centres. Yet, over time, some benign tumours can become malignant. Malignant brain tumours, on the other hand, are formed by cells that typically grow quickly and are capable of invading nearby tissues and spreading to other parts of the body. Their tendencies to attack and spread make these cancers much more dangerous. Malignant tumors are often spread to other parts of the central nervous system. Only few spread to other parts of the body. The cause of most of the brain cancers are unknown. Altogether, cancers are due to a combination of inherited genetic factors joined with some contact during life, such as exposure to a chemical, a virus or radiation. Of these, the best case is of exposure to high doses of radiation, such as those given as part of cancer treatment, and an increased risk of subsequent brain cancer. Exposure to few chemicals in the workplace has also been found to increase the risk of emerging brain cancer. Infections may play a major roll as well: the virus that causes mononucleosis, the Epstein-Barr virus, has been linked to an increased risk of a form of lymphoma that affects the central nervous system, CNS lymphoma, which also is more common among individuals infected with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. Genetics play a mainly important role in a number of brain tumors that are clearly linked to a number of inborn disorders and disorders due to gene injury.
Track 9: Neuroplasticity
The current neuroscience research evidences that Neuroplasticity is the basis for brain working out exercises which reformed brain health and science investigation. The capability of the Brain to modify at any age is referred to as Neuroplasticity or Brain Plasticity. There are about 600 Neurological disorders and roughly 50 million Americans are being affected each year. The key risk factors for Neurological disorders are genetic manipulation, age, routine life and other eco-friendly agents. Abnormalities in structural and biochemical functions cause various indications. Few of them are paralysis, seizures, confusion, muscle weakness and altered levels of consciousness. One of the significant principles underlying neuroplasticity is based on the information that individual synaptic contacts are constantly being detached or recreated, largely in need upon the activity of the neurons that bear them. The activity-dependence of synaptic plasticity is taken in the aphorism which is often used to summarize Hebbian theory: "neurons that fire together, wire together"/"neurons that fire out of sync, fail to link". If two nearby neurons frequently produce an impulse in close temporal proximity, their functional properties may meet. Conversely, neurons that are not regularly activated simultaneously may be less likely to functionally meet.
Track 10: Neuroprotection
Neuroprotection proposes to the relative storing of neuronal structure and/or role. In the case of an on-going insult (a neurodegenerative insult), the relative conservation of neuronal integrity suggests a reducing rate of neuronal loss over time, which can be expressed as a differential equation. It is a broadly discovered treatment option for many central nervous system (CNS) disorders counting neurodegenerative diseases, spinal cord injury, stroke, traumatic brain injury and acute management of neurotoxin consumption (i.e. methamphetamine overdoses). Neuroprotection objectives to prevent or slow disease progression and secondary injuries by halting or at least reducing the loss of neurons. In spite of contrasts in indications or wounds related to CNS clutters, numerous of the instruments behind neurodegeneration are the same. Mutual devices incorporate expanded levels in the oxidative stretch, mitochondrial brokenness, excitotoxicity, provocative changes, press amassing, and protein aggregation. Of these devices, neuroprotective medications regularly mark oxidative stretch and excitotoxicity—both of which are significantly related with CNS disarranges. Not as it was can oxidative stretch and excitotoxicity trigger neuron cell passing but when joint they have synergistic impacts that cause indeed more debasement than on their own. In this way limiting excitotoxicity and oxidative push may be an extraordinarily vital perspective of neuroprotection. Mutual neuroprotective medications are glutamate rivals and cancer prevention agents, which point to make excitotoxicity and oxidative.
Track 11: Neuroimmunology and Neurotransmitters
Neuroimmunology is a arena merging neuroscience, the study of the nervous system, and immunology, the study of the immune system. Neuroimmunologists seek to better understand the interactions of these two complex systems during development, homeostasis and answer to injuries. A long-term goal of this rapidly developing study area is to more develop our understanding of the pathology of certain neurological diseases, some of which have no clear aetiology. In doing so, neuroimmunology subsidizes to the expansion of new pharmacological actions for several neurological conditions. Several kinds of connections include both the nervous and immune systems including the physiological functioning of the two systems in health and disease, malfunction of either or both the systems that lead to disorders and the physical, chemical, and ecological stressors that affect the two systems on a daily basis. Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that enable neurotransmission. It is a type of chemical messenger which conveys signals across a chemical synapse, such as a neuromuscular connection, from one neuron (nerve cell) to another "target" neuron, muscle cell, or gland cell. Neurotransmitters are unrestricted from synaptic vesicles in synapses into the synaptic cleft, where they are established by neurotransmitter receptors on the target cells. Various neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and abundant precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available from the diet and only require a small number of biosynthetic steps for alteration. Neurotransmitters shows a major role in shaping normal life and functions. Their exact numbers are unknown, but more than 200 chemical messengers have been exclusively recognized.
Track 12: Pediatric Stroke and Recovery
The main cause for death in children in the USA is due to stroke and the most pediatric stroke fighters will be suffering from neurological or cognitive impairments. Because of the plasticity of the brains of children, they recover faster than adults. A stroke survivor may be diagnosed with Epilepsy. Based on the cause of the stroke, the treatments will be decided by the physicians. Constraint therapy is an old one, but it is now widely used in pediatric stroke rehabilitation. If the stroke is caused by the blockage, then blood thinning medications will be given. If a stroke occurs due to Sickle Cell Disease (SCD), then an immediate blood transfusion will be performed. A physiotherapist can help with movement difficulties such as weakness or paralysis, spasticity or muscle spasms. The psychotherapist will assess and design a program to rise muscle strength (which can reduce the risk of spasticity) and movement. It is valued that about 6 million deaths are due to cerebrovascular disorders. It is the second foremost cause of death in the world and 6th most common reason of disability.
Track 13: Neuropsychiatry
Neuropsychiatry led the recent disciplines of psychiatry and neurology, which had mutual training; however, psychiatry and neurology later split apart and are typically practiced separately. Neuropsychiatry is systematically associated with the arenas of behavioral neurology. Neuropsychiatry is the line of Psychiatry and Neurology that deals with mental disorders, which in most cases can be exposed to have their beginning from an perceptible brain malfunction. Neuropsychiatry focuses to understand the connection between the mind, body and its behavior. Training in both neurological and psychiatric features of illness places Neuropsychiatry in a unique place to deliver this care. An actual assessment of the clinical course of diseases requires the application of very specific diagnostic and assessment approaches as early as possible. By attaining these strategies, offers new probabilities for biomarker identification and/or discovery in complex diseases and may provide pathological pathways empathetic for diseases beyond traditional practices.
Track 14: Stroke Nursing and Interventions
Nurses play a vital role in all phases to care of the stroke patient. Few nurse caring plans are Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion, Reduced Physical Mobility, Weakened Verbal Communication, Disturbed Sensory Perception, Ineffective Coping, Self-Care Deficit, and Risk for Reduced Swallowing. Nurses may work as an emergency medical specialist (EMT) and paramedics, radio providers of online medical control to emergency medical services (EMS) personnel from base positions, and educators who teach EMS peoples about stroke and the care of stroke patients. Nurse Interventions are monitoring key signs in patients such as checking blood pressure, associating Blood Pressure reading in arms, heart rate, rhythm and murmurs. There also look after Respirations, noting patterns and rhythm, Cheyne-Strokes respiration.
Related Conferences:
- 26th Cognitive Neuroscience Congress, June 17-18, 2019 Dubai, UAE
- 30th International Conference on Public Mental Health and Neuroscience, June 17-18, 2019 Dubai, UAE
- 2nd World Congress on Epilepsy and Brain Disorders, November 21-22, 2019 Bali, Indonesia
- 2nd World Brain Congress, December 05-07, 2019 Abu Dhabi
- 2nd World Heart and Brain Conference, December 09-10, 2019 Abu Dhabi, UAE
- 13th Global Neurologists Meeting on Neurology and Neurosurgery, November 07-08, 2019 Frankfurt, Germany
- 4th World Congress on Pediatric Neurology and Pediatric Surgery, August 12-13, 2019 Auckland, New Zealand
- 14th International Conference on Neurology, Neuroscience and Neuromuscular Disorders, June 17-18, 2019, Tokyo, Japan
- 28th Euro-Global Neurologists Meeting, June 13-14, 2019 Barcelona, Spain
- 10th IBRO World Congress of Neuroscience, September 21-25, 2019, Daegu, South Korea
- 42nd Annual Meeting of the Japan Neuroscience Society, July 25-28, 2019 Niigata, Japan
Importance and Scope:
The global neurobiology market size was valued at USD 28.42 billion in 2016 and is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 3.1% over the forecast amount. High influencing aspects, like current brain recording investigation and investigation comes, neuroscience-based initiatives by management bodies, and technological advances in tools and algorithms that are required in neurobiology. These factors are anticipated to bolster revenue generation by encouragement the merchandise adoption during this market throughout the forecast year.
Presence of organizations & institutes, such as NIH, NeuroScience Canada, University of Utah, Max Planck Florida Institute, Ontario Brain Institute, and the University of Pennsylvania; in the space are expected to majorly impact the development of neuroscience arena. These entities play a vital role in fast neuroscience-based analysis and advance to boost patient outcomes in those full of medicine disorders.
Numerous steps are undertaken by the aid communities to require brain-related studies and innovations a step additional. For example, in 2014, University of Utah launched the “Neuroscience Initiative” in order to help alleviate the devastating effects of brain disorders. The initiative was created for extending the understanding of the significances of brain disorders on health and channelizing the information into advanced solutions for patient care. Constant summary of novel merchandise by key participants within the market to combat varied medicine disorders is predicted to spice up Y-O-Y growth of this market.
For example, in September 2015, Codman Neuro announced CODMAN CERTAS plus programmable valve, an MRI-resistant programmable valve with eight different pressure settings. This product was introduced hydrocephalus treatment. Furthermore, key factor that has accelerated the research studies in this arena is the growth in number of various malignant CNS disorders such as Parkinsonism and Alzheimer’s disease. As geriatric population is liable to varied central nervous systems associated disorders like schizophrenic disorder, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinsonism, with growth in older population, this market is anticipated to witness lucrative growth.
Neurology Hospitals in UAE
- Asala Medical Center
- Berlin Medical and Neurological Rehabilitation
- Neuro Spinal Hospital
- American Center for Psychiatry & Neurology
- Burjeel Neuro Rehabilitation and Physiotherapy Center
- August Medical cereneo Center for Neurological Rehabilitation
- German Neuroscience Center
- American Center Psychiatry and Neurology
- German Neuroscience Center
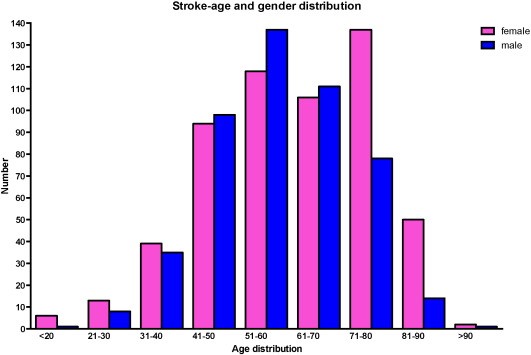
Age Factor in Stroke:
Associations and societies in Dubai
- Emirates Neurology Society
- Emirates Medical Association
- The Middle East North Africa Stroke Organization
- Shaikh Khalifa Stroke Institute
- Child Neurology Association (ICNA)
Associations and societies in UAE
- Association for Infant Mental Health
- National Association for Mental Health
- The brain & behavior research foundation
- Migraine Trust
- The Brain injury association
- The Neuro Association
Associations and societies worldwide:
- World Federation of Neurology
- Association of Neurological Surgeons
- European Federation of Neurological Societies
- The International Child Neurology Association
- Education in child neurology: the role of the International
- Child neurology services in Africa
- Neuropathy Association
- Alzheimer's Association
- American Academy of Neurology
- European Neurological Societies
- Spanish Society of Neurology
- Major Neurological Associations in Italy
- Hilarescere Foundation in Italy
- Italian MS society in Italy
- Southern Clinical Neurological Society
- ESNR European Society of Neuroradiology
- The British Neuropsychiatry association
- British Neuroscience Association
- British Neuro-oncology Society
- Brain Injury Association of London
- Stroke Association
- Brain Injury Rehabilitation Trust
- Royal Society of London
- Alzheimer's Society
- International Headache Society
- Huntington's disease Association
- Brain tumor organizations
- National Brain Tumor Society
- British neuroscience association
- British brain tumor association
- Scottish Association for Mental Health
Market Growth of Neuroscience:
The global neuroscience market size was valued at USD 28.42 billion in 2016 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.1% over the forecast period. High influencing factors, such as on-going brain mapping research and investigation projects, neuroscience-based initiatives by government bodies, and technological advances in tools and algorithms that are implemented in neuroscience space, are expected to propel the market growth.
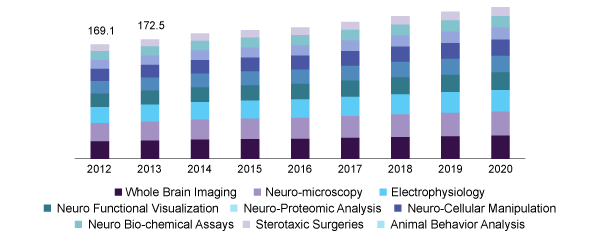
Neuroscience Market size by technology 2012-2020 (USD Million)
Universities associated with Neurology and Neurosurgery in Dubai
- King Saud University
- United Arab Emirates University
- King Abdulaziz University
- Ain Shams University
- Alfaisal University
- Middlesex University
Universities associated with Neurology and Neurosurgery in UAE
- Gulf Medical University
- RAK Medical & Health Sciences University
- Mohammed Bin Rashid University of Medicine
- College of Medicine University of Sharjah
- NYU Abu Dhabi
- Zayed Universities
- Kuwait University
- New York University Abu Dhabi
- University of Sharjah
- Abu Dhabi University
Universities associated with Neurology and Neurosurgery Worldwide:
- Stanford University
- University of California
- University of South Carolina Beauport
- University of Helsinki
- California Institute of Technology
- Yale University
- Harvard University
- University of Pennsylvania
- University of Chicago
- The Kavli Institute for Brain Science
- Cornell University
- Dalhousie University
- Leiden University- Neither land
- Temple University USA
- University Oklahoma
- Boston Coll USA
- Florida International University
- American University of Beirut
- Mansoura University
- Assiut University
- University of Edinburgh
- University of Manchester
- Cardiff University
- University of Vermont
- University of Amsterdam
- Ghent University
- Maastricht University
- University of Melbourne
- University of Queensland
- University of New South Wales
- University of Adelaide
- University of Sydney
- United Arab Emirates University
- German Neuroscience Center
Who to attend:
Neurophysiologists, Neurologists, Paediatric Neurologists, Neurosurgeons, physiatrists, Research scientists, Neurology Organizations, and Epileptologists Pharmaceutical companies, Neuro and CNS drug Industries, Neuroscience associations, Neuroscience foundations, neuroradiologists, Professors, Students from Academia in the study of Neurology and Neurophysiology and researchers who utilize neurophysiological techniques and also knowledge in diagnosing and in treating nervous system disorders, social workers.
Why to attend?
Neuology and Therapeutics is a unique forum to bring together worldwide distinguished academics in the field of neuroscience and neurology, Brain researchers, public health professionals, scientists, academic scientists, industry researchers, scholars to exchange about state of the art research and technologies.Aim of this conference is stimulate new ideas for treatment that will be beneficial across the spectrum of Brain disorders.
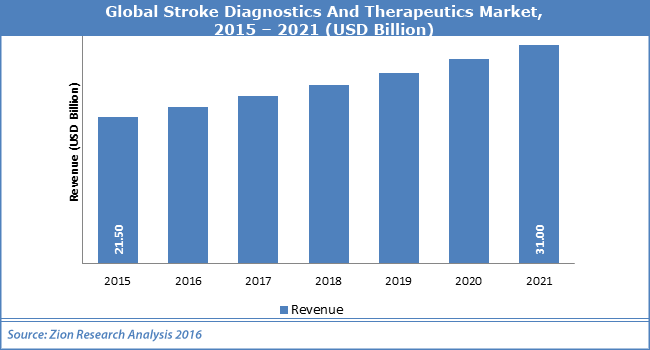
Global Market Analysis of Stroke and Neurological Disorders:
The market analysis of stroke and neurology represent the largest and untapped market in medicine sector. This estimated market analysis is based on probability of approval and sales of products in late stage development, demographic trends and marketing of product. Emerging markets once again helps to boost revenues. CNS therapeutics comprise approximately 15% of total pharmaceutical sales, nearly $30 billion worldwide.
An estimated annual economic costs of anxiety disorders, depression, and schizophrenia are $47 billion, $44 billion, and $33 billion per year approximately. The goal of this session is to understand the market Value & Growth of Neurology Drugs , Current economics cost of clinical research and development.
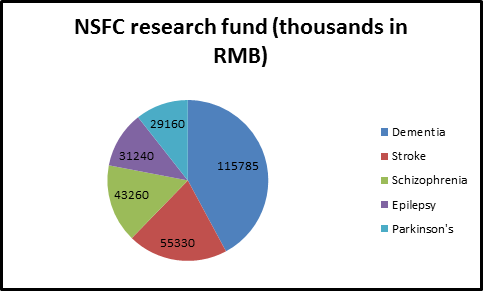
Fig: Global analysis of stroke and neurological disorders.
Associations:
Asia Pacific & Middle East:
Emirates Neurology Society (EMINS) | Emirates Nursing Association,Emirates Cardiac Society | Association of Neurophysiological Scientists | Iraqi Neurological Association (INA) - Iraq (IQ) | Israel Society for Neuroscience - Israel (IL) Society for Arab Neuroscientists | Middle East Spine Society | Mediterranean Neuroscience Society | North Africa and the Middle East - Society for Neuroscience | The Pan Arab Neurosurgical Society | Emergence of Cognitive Neuroscience in The Middle East | Middle East Neurosurgical Society | The Saudi Critical Care Society | Walter E. Dandy Neurosurgical Society | Philippine Neurological Association (PNA) | Malaysian Society of Neurosciences | Neurological Society of India | Neurological Surgeon Society of India (NSSI) | Clinical Neuroscience Society Singapore | The Japan Stroke Society | Asian Pacific Society for Neurochemistry | Indian Society of Neuro-Oncology |Indian Pharmacological Society
USA:
American Stroke Association | National Stroke Association | Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada | North Carolina Stroke Association | American Association of Neurological Surgeons | American Academy of Neurology | Canadian Stroke Consortium | Canadian Stroke Network | Intermountain Stroke Center | National Stroke Association | Merican Society of Neuro-rehabilitation | USAAneurysm Foundation& Brain Injury Association of America | Huntington's Disease Society of America and Hydrocephalus Association | United Spinal Association& Vascular Birthmarks Foundation | American Society for Neurochemistry | The Canadian Society of Pharmacology and Therapeutics | American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutic | Epilepsy Foundation of America.
Europe:
German Stroke Society | European Stroke Organization | World Federation of Neurology | World Stroke Organization | The Brain Injury Association | Mediterranean Stroke Society | European Federation of Neurological Associations | Spanish Society of Neurology | European neurological society | European Academy of Neurology | National Stroke Association of Russian Federation | Central and East European Stroke Society | Romanian National Stroke Association (RNSA) | British Columbia Society of Electroneurophysiology | Technologists Alzheimer Europe | British Columbia Society of Electro Neurophysiology Technologists | British Paediatric Neurology Association | The British Association of Stroke Physicians | Danish Neurological Society | Dutch Society of Neurology | The Association of British Neurologists | British Neuro-Oncology Society | Italian Neurological Society| Italian Stroke Society | British Acoustic Neuroma Association (BANA)(UK)
Conference Highlights
- Stroke and Mental Health
- Neurological Disorders
- Stroke and Cardiovascular Diseases
- Brain and Neuromuscular Diseases
- Stroke Rehabilitation and Recovery
- Epidemiology
- Neurophysiology and Neurodegeneration
- Brain Tumor and Neuro oncology
- Neuroplasticity
- Neuroprotection
- Neuroimmunology and Neurotransmitters
- Pediatric Stroke and Recovery
- Neuropsychiatry
- Stroke Nursing and Interventions
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | December 02-03, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by