Theme: Building a Better World without Disorders
Stroke Meet 2018
We take immense pleasure in inviting all the participants from all over the world to attend the Neuroscience conference entitled “5th Annual Conference on Stroke and Neurological disorders ” to be held on November 12-13, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey
Stroke Meet 2018 has been planning and aiming to stimulate new techniques for treatment of Stroke and Neurological disorders that would be beneficial for the neurosurgery and other neurological issues.
The conference will be coordinated around the theme ‘Building a Better World without Disorders’.
Our goal is to bring together worldwide distinguished academics in the field of Neurology and Brain to exchange and share meaningful experiences of various treatment procedures for Neurological disorders and Stroke.
Scope and Importance
While more people are surviving strokes, many still face long-term disability. Stroke Meet 2018 provides a platform for all the Neurology professionals, Researchers and Scientists to share knowledge and overcome this disorder by Innovative and Nobel ideas in Diagnosis and Treatment.
Target Audience
- Neurologists and Researchers
- Neurology Faculty and Students
- Doctors and Scientists
- Universities, Associations and Societies
- Students and Research Scholars
- Business Delegates
- Product Manufacturer
Track 1: Neurological Disorders
Any disorder of the nervous system is called as neurological disorder. Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves can result in a number of symptoms for example paralysis, muscle weakness, problem in coordination, loss of sensation, confusion, pain and altered levels of consciousness., some neurological disorders are relatively common and many are rare. They may be determined by neurological examination, and studied and treated within neurology and clinical neuropsychology.Neurological disorders involve physiotherapy or other therapy, neurorehabilitation, life style changes medication, or operations performed by neurologists.
Track 2: Stroke and It's Management
A stroke is a restorative crisis. Strokes happen when bloodstream to your mind stops. Inside minutes, cerebrum cells start to kick the bucket. There are two sorts of stroke. The more normal kind, called ischemic stroke, is created by a blood coagulation that squares or attachments in a vein in the cerebrum. The other kind, called hemorrhagic stroke, is brought on by a vein that breaks and seeps into the cerebrum. "Smaller than normal strokes" or transient ischemic assaults (TIAs), happen when the blood supply to the cerebrum quickly interferes. Stroke is the third driving reason for death in the United States. Of the more than 700,000 individuals influenced each year, around 500,000 of these are first assaults, and 200,000 are intermittent. It is estimated that about 29 percent of individuals who recuperate from their first stroke will face another stroke inside four to five years. Stroke is the main source of genuine long haul handicap, with an expected 5.4 million stroke survivors presently alive today.
Track 4: Stroke Rehabilitation and Brain Haemorrhage
Rehabilitation is given for long period of time to improve function so that the stroke survivor can become as independent as possible. This must be accomplished in a way that preserves dignity and motivates the survivor to relearn basic skills that the stroke may have impaired - skills like bathing, eating, dressing and walking. Rehabilitation starts in the hospital as soon as possible following a stroke. The rehab team includes Physiatrist, Neurologist, Rehabilitation Nurse, Physical Therapist, Occupational Therapist and Speech-Language Pathologists. Cerebrovascular refers to blood flow in the brain. Arteries supplying oxygen to the brain are affected and bring about one of a number of cerebrovascular diseases. Most common is a stroke or mini-stroke and sometimes can be a hemorrhagic stroke. Cerebrovascular diseases include carotid stenosis, vertebral stenosis and intracranial stenosis, aneurysms, and vascular malformations. Restriction in blood flow can be caused by vessel narrowing, clot formation, blockage or blood vessel rupture.
It is estimated that about 6 million deaths are due to cerebrovascular disorders. It is the second leading cause of death in the world and 6th most common cause of disability.
Track 5: Neurophysiology and Neurodegeneration
Neurophysiology is a branch of physiology and neuroscience that is concerned with the study of the functioning of the nervous system. The primary tools of basic neurophysiological research include electrophysiological recordings for example, voltage clamp,patch clamp, extracellular single-unit recording and recording of local field potentials, as well as some of the methods of apoptogenesis, calcium imaging, and molecular biology.Neurophysiology is related to electrophysiology, neuroanatomy, psychology and mathematical neuroscience.Neurodegeneration is the process of progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, including death of neurons. Many neurodegenerative diseases – including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and Huntington's – occur as a result of neurodegenerative processes. Such diseases are incurable, resulting in progressive degeneration and/or death of neuron cells. As research progresses, many similarities appear that relate these diseases to one another on a sub-cellular level. Discovering these similarities offers hope for therapeutic advances that could ameliorate many diseases simultaneously. There are many parallels between different neurodegenerative disorders including atypical protein assemblies as well as induced cell death. Neurodegeneration can be found in many different levels of neuronal circuitry ranging from molecular to systemic.
Track 6: Neuroprotection
Neuroprotection suggests to the relative storage of neuronal structure and/or function. In the case of an ongoing insult (a neurodegenerative insult) the relative preservation of neuronal integrity implies a decreasing in the rate of neuronal loss over time, which can be expressed as a differential equation. It is a widely explored treatment option for many central nervous system (CNS) disorders including neurodegenerative diseases, spinal cord injury, stroke, traumatic brain injury and acute management of neurotoxin consumption (i.e. methamphetamine overdoses). Neuroprotection aims to prevent or slow disease progression and secondary injuries by halting or at least slowing the loss of neurons. In spite of contrasts in indications or wounds related with CNS clutters, numerous of the instruments behind neurodegeneration are the same.Common instruments incorporate expanded levels in oxidative stretch, mitochondrial brokenness, excitotoxicity, provocative changes, press amassing, and protein aggregation. Of these instruments, neuroprotective medications regularly target oxidative stretch and excitotoxicity—both of which are profoundly related with CNS disarranges. Not as it were can oxidative stretch and excitotoxicity trigger neuron cell passing but when combined they have synergistic impacts that cause indeed more debasement than on their own. In this way restricting excitotoxicity and oxidative push may be a exceptionally vital perspective of neuroprotection. Common neuroprotective medications are glutamate opponents and cancer prevention agents, which point to constrain excitotoxicity and oxidative.
Track 7: Brain Tumor and Neuro oncology
Benign and malignant. Benign tumors are typically formed by slow growing cells that rarely spread. Although they can press on and damage nearby normal tissue, benign tumors are much less dangerous than malignant tumors. However, they can be life-threatening if they endanger vital brain centers. However, overtime, some benign tumors can become malignant. Malignant brain tumors, on the other hand, are formed by cells that typically grow quickly and are capable of invading nearby tissues and spreading to other parts of the body. Their tendencies to invade and spread make these tumors much more dangerous. Malignant tumors of the brain often spread to other parts of the central nervous system. Only relatively few spread to other parts of the body. The cause of most brain cancers is unknown. In general, cancers are due to a combination of inherited genetic factors coupled with some exposure during life, such as exposure to a chemical, a virus or radiation. Of these, the best case has been made for exposure to high doses of radiation, such as those given as part of cancer treatment, and an increased risk of subsequent brain cancer. Exposure to some chemicals in the workplace has also been found to increase the risk of developing brain cancer. Infections may play a role as well: the virus that causes mononucleosis, the Epstein-Barr virus, has been linked to an increased risk of a form of lymphoma that affects the central nervous system, CNS lymphoma, which also is more common among individuals infected with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. Genetics play a particularly important role in a number of brain tumors that are clearly linked to a number of inherited disorders and disorders due to chromosome damage.
Track 8: Neuropsychiatry
Neuropsychiatry is a branch of medical science that deals with diseases of the nervous system. It preceded the current disciplines of psychiatry and neurology, which had common training, however, psychiatry and neurology have subsequently split apart and are typically practiced separately. Neuropsychiatry is closely related to the fields of behavioral neurology. Neuropsychiatry is the interface of Psychiatry and Neurology that deals with mental disorders, which in most cases can be shown to have their origin from an identifiable brain malfunction. Neuropsychiatry focuses to understand the link between the mind, body and its behavior. Training in both organic (neurological) and psychiatric aspects of illness places Neuropsychiatry in a unique position to deliver this care. An effective evaluation of the clinical course of diseases requires the application of very precise diagnostic and assessment approaches as early as possible. By achieving these strategies, offers new opportunities for biomarker identification and/or discovery in complex diseases and may provide pathological pathways understanding for diseases beyond traditional methodologies.
Track 9: Stroke Nursing and Interventions
Nurses play a important role in all phases of care of the stroke patient. Some of the nurse caring plans are Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion, Impaired Physical Mobility, Impaired Verbal Communication, Disturbed Sensory Perception, Ineffective Coping, Self-Care Deficit, and Risk for Impaired Swallowing. Nurses may work as an emergency medical technician (EMT) and paramedics, radio providers of online medical control to emergency medical services (EMS) personnel from base stations, and educators who teach EMS personnel about stroke and the care of stroke patients. Nurse Interventions are monitoring major signs in patients such as monitoring blood pressure, comparing BP reading in arms, heart rate, rhythm, and murmurs. There also monitor Respirations, noting patterns and rhythm, Cheyne-Strokes respiration.
Track 10: Neuroplasticity and Blood Brain Barrier
There are about 600 Neurological disorders and approximately 50 million Americans are being affected each year. The main risk factors for Neurological disorders are genetic manipulation, age, lifestyle and other environmental agents. Abnormalities in structural and biochemical functions cause various symptoms. Some of them are paralysis, seizures, confusion, muscle weakness and altered levels of consciousness.The ability of the Brain to alter at any age is referred to as Neuroplasticity or Brain Plasticity. The recent neuroscience research proves that Neuroplasticity is the basis for brain training exercises which revolutionized the brain health and science research.
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane barrier that separates the circulating blood from the brain and extracellular fluid in the central nervous system (CNS). The blood–brain barrier is formed by brain endothelial cells and it allows the passage of water, some gases, and lipid-soluble molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective transport of molecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. Furthermore, it prevents the entry of lipophilic potential neurotoxins by way of an active transport mechanism mediated by P-glycoprotein. Astrocytes have been claimed to be necessary to create the blood–brain barrier. A few regions in the brain, including the circumventricular organs, do not have a blood–brain barrier.
Track 11:Neuroimmunology and Neurotransmitters
Neuroimmunology is a field combining neuroscience, the study of the nervous system, and immunology, the study of the immune system. Neuroimmunologists seek to better understand the interactions of these two complex systems during development, homeostasis, and response to injuries. A long-term goal of this rapidly developing research area is to further develop our understanding of the pathology of certain neurological diseases, some of which have no clear etiology. In doing so, neuroimmunology contributes to development of new pharmacological treatments for several neurological conditions. Many types of interactions involve both the nervous and immune systems including the physiologicalfunctioning of the two systems in health and disease, malfunction of either and or both systems that leads to disorders, and the physical, chemical, and environmental stressors that affect the two systems on a daily basis.
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that enable neurotransmission. It is a type of chemical messenger which transmits signals across a chemical synapse, such as a neuromuscular junction, from one neuron (nerve cell) to another "target" neuron, muscle cell, or gland cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles in synapses into the synaptic cleft, where they are received by neurotransmitter receptors on the target cells. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available from the diet and only require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters play a major role in shaping everyday life and functions. Their exact numbers are unknown, but more than 200 chemical messengers have been uniquely identified.
Track 12:Pediatric Stroke and Recovery
The main reason of death in children in the USA is due to stroke and the most pediatric stroke survivors will be suffering from neurological or cognitive impairments. Because of the plasticity of the brains of children, they recover faster than adults. A stroke survivor may be diagnosed with Epilepsy. Based on the cause of the stroke, the treatments will be decided by the physicians. Constraint therapy is an old therapy, but it is now extensively used in the pediatric stroke rehabilitation. If the stroke is caused by the blockage, then blood thinning medications will be given. If stroke happens due to Sickle Cell Disease (SCD), then an immediate blood transfusion will be performed. A physiotherapist can help with movement problems such as weakness or paralysis, spasticity or muscle spasms. The therapist will assess and design a program to improve muscle strength (which can reduce the risk of spasticity) and movement.
It is estimated that about 6 million deaths are due to cerebrovascular disorders. It is the second leading cause of death in the world and 6th most common cause of disability.
Track 13: Cerebrovascular Disorders
Cerebrovascular disease is a medical conditions that affect the blood vessels of the brain and the cerebral circulation. The arteries supplying oxygen and nutrients to the brain are usually get damaged in this disorders. The most common type of cerebrovascular disease is an ischemic stroke or mini-stroke and sometimes a hemorrhagic stroke. high blood pressure (Hypertension) is the most important contributing risk factor for stroke and cerebrovascular diseases as it can change the structure of blood vessels and result in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a condition where the blood vessels narrows in the brain, resulting in decreased cerebral perfusion. Narrowed cerebral arteries may lead to ischemic stroke, but continually elevated blood pressure can also cause tearing of vessels, leading to a hemorrhagic stroke.
Track 14: Clinical Trials in Neurology
Clinical trials and research are an important part of the Department of Neurology. This clinical trial will lead to the new discovery that eventually improves the patient health. Clinical trials allow researchers to study new treatment options, drugs or combinations of treatments to determine if they can be integrated into a standard practice of care. A list of active clinical trials is provided below. Many research trials have been conducted in each department of neurology to ensure the safety and advancement of patient care.
Track 15: Preventation and Control of Neurological Disorders
The anticipation of neurological infection within the post-infant stage of life and considers both the open wellbeing and person procedures that have been utilized for essential avoidance. Auxiliary avoidance is considered for certain conditions—for example, stroke. To be able to plan essential preventive techniques, sound epidemiological prove is required. Components to consider are case definition, ponder plan, and the resultant certainty with which elucidation of the comes about can be made. For numerous of the neurological conditions talked about case definition is risky. In stroke, for case, a clinical definition is utilized in most investigate thinks about. For numerous neurological conditions there are point by point clinical case arrangement but when surveying dangers, most prove has been based on case-control considers with the resultant biases. This survey essentially considers stroke, because it is the major cause of grown-up neurological passing and inability. With current information of chance variables it is the condition in which there's most scope for essential avoidance. A brief survey of a few of the other major neurological maladies is included to demonstrate regions where work has been detailed or is required. The viewpoint in this survey is that of the created world.
Stroke Meet 2018 welcomes attendees, presenters, and exhibitors from all over the world to Istanbul, Turkey. We are delighted to invite you all to attend and register for 5th Annual Conference on Stroke and Neurological Disorders having the theme “Building a Better World without Disorders” which is going to be held during November 11-13, 2018 at Istanbul, Turkey.
The organizing committee is gearing up for an exciting and informative conference program including plenary lectures, symposia, workshops on a variety of topics, poster presentations and various programs for participants from all over the world. We invite you to join us at the Stroke Meet 2018, where you will be sure to have a meaningful experience with scholars from around the world.
Scope and Importance
Stroke Meet 2018 aims to bring together leading academic scientists, researchers, and research scholars to exchange and share their experiences and research results about all aspects such as; Advances in Prevention, Treatment, and Recovery in Stroke and other Neurological disorders. It also provides the premier interdisciplinary forum for researchers, practitioners, and educators to present and discuss the most recent innovations, trends, and concerns, practical challenges encountered and the solutions adopted in the field of Stroke and Neurological Disorders.
Neuro disorders are the disorders of brain, spine and nerve cells. It occurs due to the faulty genes and by muscular dystrophy. Damage to the nerve cell or death of the nerve cell causes degenerative disorders such as Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. Diseases of the blood vessels that supply the brain, include stroke, Injuries to the spinal cord and brain Seizure disorders, such as epilepsy Cancer etc. The persons suffering from Neuro disorders have poor judgment, relapsing of memory, Tremor, Loss of automatic movement, Speech changes, rigid muscle etc. So this conference will provide novel technologies in the development of Neurology and neuro disorders.
Report Highlights
- The global market for neurological disease treatment and medication was worth $12.6 billion in 2006 and reached $14 billion by 2007. At a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.6%, the global market will be worth almost $42.3 billion by 2022.
- Drugs for multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease control approximately 99% of the total market share.
- Medications for multiple sclerosis are just over 35% greater than the market share of medication for Alzheimer's disease, despite the fact that there are far fewer patients with MS. As AD drugs become more prevalent, the shares of the market could change dramatically
Why Turkey
Turkey has an interesting key position at the junction of East and West which enriches this nation with about ten-thousand years of history. As a feature of Asia and part of Europe, Turkey has strikingly wide climatic and topographical varieties. Because of its area, encompassed via oceans on three sides, Turkey as dependably been the focal point of extraordinary exchange, silk, and zest courses. The nature of the training and showing staff at Turkish Universities offers you a universe of chances to get the right stuff you will require for a worldwide world. In Turkey, understudies will have the chance to encounter both advancement and custom in one of the most secure and most stable nations in the locale. Individuals from everywhere throughout the world visit Istanbul city due to its extremely extraordinary area, religious importance, history and less expensive costs contrasted with other European urban areas. Istanbul stays aware of the advancements and improvements in the tourism part while safeguarding its social heritage. Above all, the high caliber of training will make you prepared for what's to come.
Who to attend:
Neurophysiologists, Neurologists, Paediatric Neurologists, Neurosurgeons, physiatrists, Research scientists, Neurology Organizations, and Epileptologists Pharmaceutical companies, Neuro and CNS drug Industries, Neuroscience associations, Neuroscience foundations, neuroradiologists, Professors, Students from Academia in the study of Neurology and Neurophysiology and researchers who utilize neurophysiological techniques and also knowledge in diagnosing and in treating nervous system disorders, social workers.
Why to attend???
Neuology and Therapeutics is a unique forum to bring together worldwide distinguished academics in the field of neuroscience and neurology, Brain researchers, public health professionals, scientists, academic scientists, industry researchers, scholars to exchange about state of the art research and technologies.
Aim of this conference is stimulate new ideas for treatment that will be beneficial across the spectrum of Brain disorders
Top Neurology Universities in Globe:
- Leiden University
- Keele University
- Plymouth University
- University of Toledo
- University of Sheffield
- University of Birmingham
- University of Windsor
- University of Edinburgh
- University of California Irvine
- University of Nottingham
- New York University
Top Neuroscience University in Turkey
- Georgetown university medical center
- Bahcesehir university
- Yeditepe university
The Turkish Neurosurgical Societies
1. Spine and Peripheral Nerve Surgery Section
2. Pediatric Neurosurgery Section
3. Neuro-oncologic Surgery Section (incl. Skull base Surgery Section)
4. Neurotrauma and Intensive Care Section
5. Neurovascular Surgery Section
6. Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery Section (incl. Pain and Epilepsy surgery)
7. Surgical Neuro-anatomy Section
Much of the important work of the TNS has been the job of its different committees.
Currently, there are some TNS committees; some of them are as follows;
1. Education and Training Board
2. Board of the Turkish Neurosurgical Society Publications
3. Basic Course in Neurosurgery Working Group
4. The Turkish Board of Neurosurgical Surgery
5. Ethics Committee
6. External Relations Committee
7. Young Neurosurgeons Committee
8. Social Affairs and Relations Committee
9. Professional Personnel Rights Committee
10. Malpractice, Finance, Insurance & Legal Committee
11. Awards and Scholarship Program Assessment Committee
12. Long Term Planning Committee
Global Market Analysis of Stroke and Neurological Disorders
The market analysis of stroke and neurology represent the largest and untapped market in medicine sector. This estimated market analysis is based on probability of approval and sales of products in late stage development, demographic trends and marketing of product. Emerging markets once again helps to boost revenues. CNS therapeutics comprise approximately 15% of total pharmaceutical sales, nearly $30 billion worldwide.
An estimated annual economic costs of anxiety disorders, depression, and schizophrenia are $47 billion, $44 billion, and $33 billion per year approximately. The goal of this session is to understand the market Value & Growth of Neurology Drugs , Current economics cost of clinical research and development.
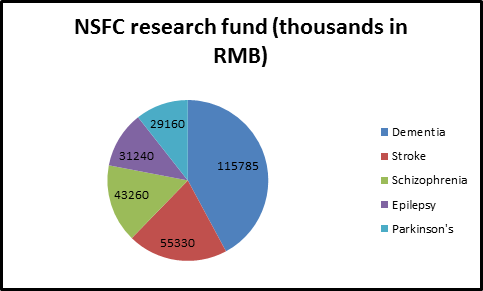
fig : global analysis of stroke and neurological disorders.
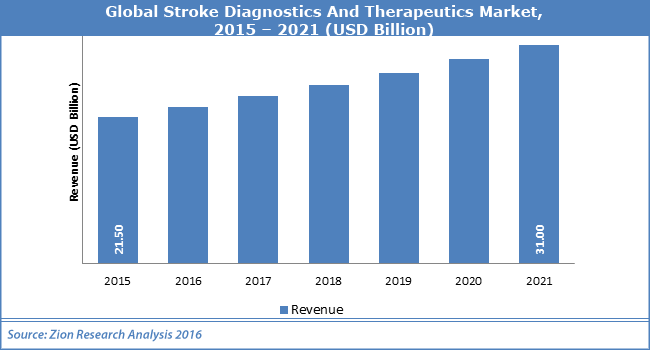
fig: Global Stroke Diagnostics and Therapeutics market ,2015-2021
Related Conferences:
- 31st Clinical Neuroscience and Neurogenetics Conference: Mobilizing Neurons to Rehabilitate, August 13-14, 2018 Dubai, UAE
- 25th International Conference on Neurochemistry and Neuropharmacology, September 17-18, 2018 Dubai, UAE
- International Child and Adult Behavioral Health Conference. September 13-14, 2018, Dubai.UAE
- 25th International Conference on Neurochemistry and Neuropharmacology, September 17-18, 2018 Dubai, UAE
- 3rd International Conference on Neurooncology and Neurosurgery, September 20-21, 2018 Dubai, UAE
- 30th International Conference on Psychiatry and Mental Health, October 11-12, 2018 Dubai, UAE
- 8th International Congress on Stroke and Brain Hemorrhage. September 20-21,Prague | Czech Republic
- 31st clinical Neuroscience and Neurogenetics conference: Mobilizing Neurons to Rehabilitate. August 13-14,2018 Dubai, UAE.
- International Conference on Neurooncology and Neurosurgery. September 17-18, Dubaii UAE.
- 29th Jnternational conference on psychiatry & Mental Health. September 14-15, Singapore .
- 18th Global Neuroscience conference, September 19-20, Japan
Associations:
USA
American Stroke Association | National Stroke Association | Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada | North Carolina Stroke Association | American Association of Neurological Surgeons | American Academy of Neurology | Canadian Stroke Consortium | Canadian Stroke Network | Intermountain Stroke Center | National Stroke Association | Merican Society of Neuro-rehabilitation | USAAneurysm Foundation& Brain Injury Association of America | Huntington's Disease Society of America and Hydrocephalus Association | United Spinal Association& Vascular Birthmarks Foundation | American Society for Neurochemistry | The Canadian Society of Pharmacology and Therapeutics | American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutic | Epilepsy Foundation of America.
Europe:
German Stroke Society | European Stroke Organization | World Federation of Neurology | World Stroke Organization | The Brain Injury Association | Mediterranean Stroke Society | European Federation of Neurological Associations | Spanish Society of Neurology | European neurological society | European Academy of Neurology | National Stroke Association of Russian Federation | Central and East European Stroke Society | Romanian National Stroke Association (RNSA) | British Columbia Society of Electroneurophysiology | Technologists Alzheimer Europe | British Columbia Society of Electro Neurophysiology Technologists | British Paediatric Neurology Association | The British Association of Stroke Physicians | Danish Neurological Society |Dutch Society of Neurology | The Association of British Neurologists| British Neuro-Oncology Society;Italian Neurological Society| Italian Stroke Society | British Acoustic Neuroma Association (BANA)(UK)
Asia Pacific & Middle East
Emirates Neurology Society (EMINS) | Emirates Nursing Association,Emirates Cardiac Society | Association of Neurophysiological Scientists | Iraqi Neurological Association (INA) - Iraq (IQ) | Israel Society for Neuroscience - Israel (IL) Society for Arab Neuroscientists | Middle East Spine Society | Mediterranean Neuroscience Society | North Africa and the Middle East - Society for Neuroscience | The Pan Arab Neurosurgical Society | Emergence of Cognitive Neuroscience in The Middle East | Middle East Neurosurgical Society | The Saudi Critical Care Society; Walter E. Dandy Neurosurgical Society; Philippine Neurological Association (PNA) | Malaysian Society of Neurosciences | Neurological Society of India | Neurological Surgeon Society of India (NSSI) | Clinical Neuroscience Society Singapore | The Japan Stroke Society | Asian Pacific Society for Neurochemistr | Indian Society of Neuro-Oncology |Indian Pharmacological Society
Conference Highlights
- Mental Health: Alzheimer’s and Dementia
- Stroke Rehabilitation and Brain Hemorrhage
- Neuroprotection
- Neurophysiology and Neurodegeneration
- Stroke and its Management
- Brain Tumors and Neuro - Oncology
- Neuroimmunology and Neurotransmitters
- Neuropsychiatry
- Stroke Nursing and Interventions
- Neuroplasticity and Blood Brain Barrier
- Pediatric Stroke and Recovery
- Clinical Trials in Neurology
- Neurological Disorders
- Prevention and Control of Neurological disorders
- Cerebrovascular Disorders
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | November 12-13, 2018 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by